Big Data and AI Redefine ICU Care Through Real-Time Risk Prediction
During the pandemic, demand for critical care surged, placing an overwhelming workload on medical staff. This prompted Taichung Veterans General Hospital (VGHTC) to consider how to leverage the large-scale data analytics it had accumulated over the years to provide early warnings of patient deterioration, enable earlier clinical intervention, support medical decision-making, and improve patient outcomes.
For these purposes, Zoe was created. Meaning “life” in Greek, it is a smart critical care system designed for ICUs, combining artificial intelligence (AI) and human intelligence (HI). This AI-assisted model provides early detection of critical conditions of patients in the emergency room.
VGHTC's achievements in smart care have earned the hospital recognition by Newsweek and research firm Statista as one of the world’s top smart hospitals.

Zoe Monitors Patients' Renal and Respiratory Conditions, Septic Shock, and Mortality Risk
Based on urgency needs in the ER, Zoe is categorized by themes, such as renal and respiratory critical care, septic shock, and mortality risk. Corresponding models are developed for acute kidney injury (AKI) risk prediction, classification of Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS), bloodstream infection risk prediction, and mortality risk prediction.
Wu Chieh-Liang, Deputy Superintendent of VGHTC and a pulmonology and critical care specialist, explained the goals behind the four themes.
First, approximately 30–50 percent of ICU patients develop AKI, making early prediction important.
Second, patients with respiratory failure who develop ARDS face a mortality rate of around 40–50 percent, highlighting the need to optimize diagnosis and treatment.
Third, for patients hospitalized for three to five days, the system assesses the likelihood of developing bloodstream infections. “If we know in advance, we can prevent it from happening, for example, by adjusting catheters early or identifying potential sources of infection,” he said.
Finally, if a patient’s prognosis is poor and mortality risk is high, the medical team can receive an alert a day in advance, allowing both the team and the family to prepare early.
Integrated Dashboards Centralize Critical Care Alerts for Comprehensive Care
Previously, patient data were scattered across the Hospital Information System (HIS), making it akin to searching for a needle in a haystack for less-experienced physicians. Integrating physicians, nurses, respiratory therapists, dietitians, and pharmacists for emergency tasks also required considerable time.
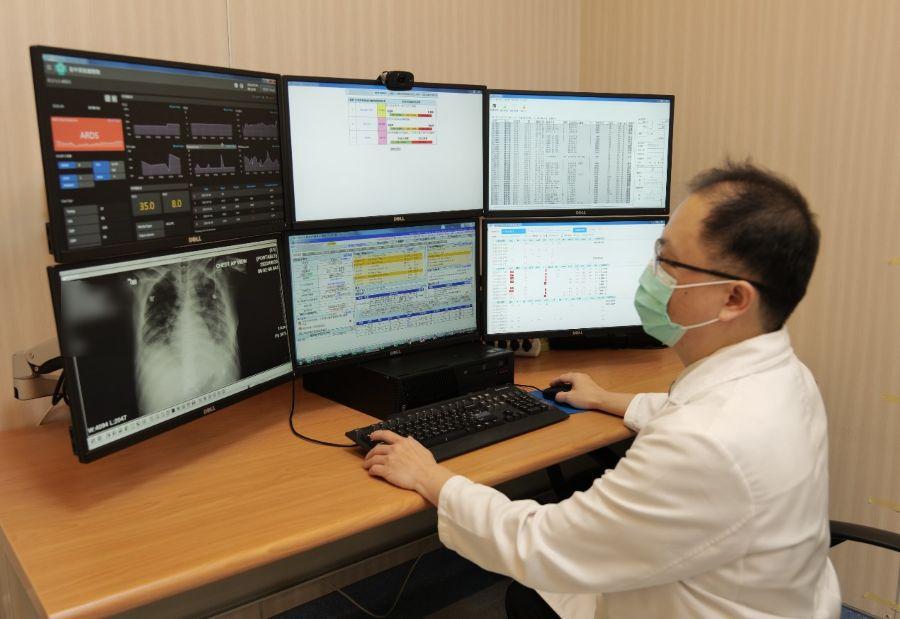
To solve the problem, VGHTC integrated its Electronic Hospital Information System (EHIS) with Advantech’s WISE-PaaS cloud platform, to provide alerts that further assist physicians’ judgment.
Chan Ming-Cheng, Director of Respiratory Intensive Care Unit, noted that visualized dashboard information facilitates smoother team communication. With everyone viewing the same information, the team can readily assess whether patient care is on track.
Using ARDS, of the common causes of death in COVID-19, as an example. Before the introduction of Zoe, therapists had to check each bed one by one during rounds. Now, the dashboard prioritizes high-risk patients, displaying ventilator parameters, imaging, heart rate, blood pressure, and other vital signs. Based on these data, respiratory therapy teams can adjust tidal volumes, neuromuscular blocking agents, and determine whether prone ventilation is indicated.
Additionally, many ICU patients face polypharmacy challenges, requiring careful avoidance of drug interactions. Wang Tsai-jung, Director of the First Medical ICU and an attending nephrologist, explained that the AKI risk prediction model helps pharmacists save time by identifying high-risk patients first, prompting alerts on nephrotoxic medications and adjustments to dosages and fluid balance.
Medicine and High-Tech Build an 80 Million–Record Critical Care Database Tailored for Taiwan
First, a team led by Lai Lai-Shiun, Director of the hospital’s Information Technology Department, undertook data-cleaning work. Physicians then defined which features should be used. Once the data were sufficiently cleaned, faculty from Department of Computer Science, Tunghai University, conducted data exploration, verified data quality, and designed training models for prediction.
In developing the ARDS model, Taichung Veterans General Hospital sought to integrate clinical data with imaging to enhance inference quality. Wu, Deputy Superintendent of VGHTC, explained that to create an image-reading model, features had to be annotated on X-ray images first.
“I reviewed nearly a thousand images, and the computer science faculty then translated that into an AI for X-ray analysis, tracking features related to ARDS within each image,” he said.
VGHTC remains to be Taiwan’s largest and most comprehensive critical care database. From 2015 to 2020, it accumulated 66.1 million data records across 24 adult ICU categories and 339 features. By 2023, the database had grown to 80 million records, supporting clinical research and AI applications.
“The database is a vital asset. Without it, computation and prediction would not be possible,” Chan noted.
VGHTC had previously used the international open database MIMIC-III and later MIMIC-IV. “However, we needed to build models suited to Taiwan’s National Health Insurance environment. Foreign models don’t necessarily fit in.” And VGHTC's solution to the problem is to build the database according to Taiwan's needs.
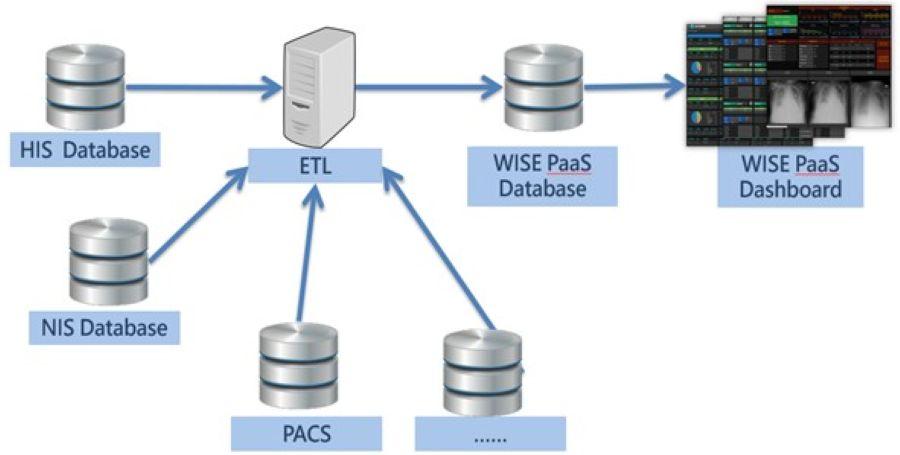
Given the diversity and volume of its data, the hospital employed Extractor, Transfer, and Loader (ETL) tools to automate inference and dashboard data transfers. Values, text, and images from multiple databases, including HIS, NIS, and PACS, are read hourly and transmitted to Advantech’s WISE-PaaS Database. When users open the dashboard, the most up-to-date data are displayed.
What lies behind today’s polished dashboards is a continual experimentation and refinement. Wu said that more models will be integrated in the future to encourage physicians, nurses, therapists, and dietitians to use the system. A feedback mechanism has also been built in, so users can comment on AI performance and achieving the integration of AI and HI. At last, technology and human wisdom can work hand in hand in the ICU.
Editor’s note: This article features a Silver Award recipient of the 25th (2022) National Biotechnology and Medical Care Quality Award. All titles mentioned reflect the positions held by interviewees at the time of the interviews.






